Building Information Modeling (BIM) is a leading technology for Architecture, Engineering, and Construction (AEC) practices playing a vital role in
facilitating projects delivery through 3D collaborative model, allowing real-time track of the project modifications and progress in different stages of its lifecycle, planning erection and logistics, optimizing costs, time and efforts, and enhancing buildings’ performance in terms of comfort, efficiency, and sustainability. Considering BIM potential, an increasing number of countries are considering its implementation as an innovative concept leading to cost-efficiency and ecological practices in the AEC industry.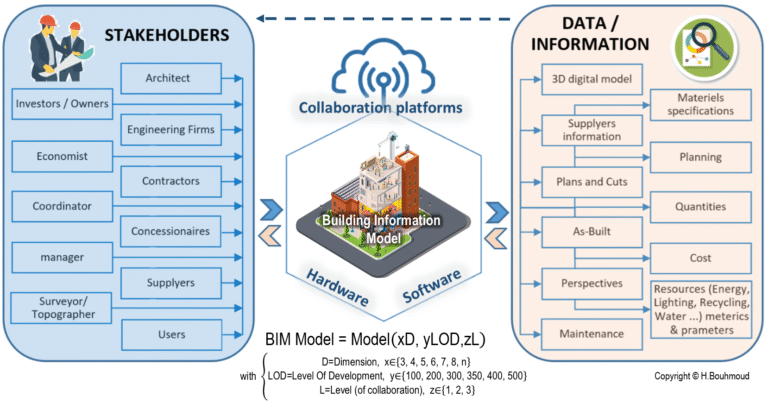
Using Building Information Modeling (BIM) enables stakeholders in Architecture, Engineering, and Construction (AEC) projects to
significantly optimize workflow, effort, and time compared to traditional practices. Collaborative BIM tools enhance design accuracy, erection quality, coordination, and communication among parties, while also improving lifecycle data management, claims management, and site and facility management.BIM facilitates
visualization of buildings before construction, allowing stakeholders to anticipate risks, save costs, and strengthen collaboration.BuildingSMART reported that BIM improved
the understanding of design intentions, overall project quality, and cost control in Europe by 69%, 62%, and 43%, respectively, and in North America by 65%, 54%, and 37%. Conversely, BIM reduced conflicts among project stakeholders, design modifications during construction, and clarification requests by 59%, 56%, and 43% in Europe, and by 68%, 54%, and 47% in North America.BIM enables designers, either architects or engineers, to
create detailed 3D models (iBIM) incorporating all necessary building elements, including floors, ceilings, and mechanical, electrical, and plumbing (MEP) networks; enabling multiparametric simulation, removal of scopes conflicts, grounded decision making, and streamlined management. This level of precision has supported the rapid completion of large-scale projects under very challenging circumstances, such as the 3.4-hectare hospital in Wuhan, China, built in just 10 days to respond to the critical COVID-19 pandemic needs.This explains the BIM’s
rapid global adoption embraced by developers, designers, contrators, and facility managers as an indispensable tool for efficiency, collaboration, and performance.To explore BIM potential for other construction aspects, consult the study in the link
To Cite this Article
Bouhmoud, H., Loudyi, D., 2021. Building Information Modeling (BIM) Framework, Potential and Challenges. International Journal of Information Science and Technology 5, 24–35. https://doi.org/10.57675/IMIST.PRSM/ijist-v5i3.173
H. Bouhmoud and D. Loudyi, “Building Information Modeling (BIM) Framework, Potential and Challenges,” International Journal of Information Science and Technology, vol. 5, no. 3, Art. no. 3, 2021, doi: 10.57675/IMIST.PRSM/ijist-v5i3.173.
Bouhmoud, H., & Loudyi, D. (2021). Building Information Modeling (BIM) Framework, Potential and Challenges. International Journal of Information Science and Technology, 5(3), Article 3. https://doi.org/10.57675/IMIST.PRSM/ijist-v5i3.173
